
Founded in 1986, the group developed the JPEG standard during the late 1980s.
#JPEG IMAGE COMPRESSION STANDARDS . PDF ISO#
The "Joint" stood for ISO TC97 WG8 and CCITT SGVIII. "JPEG" stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group, the name of the committee that created the JPEG standard and also other still picture coding standards. However, the JPEG specification did cite two earlier research papers by Wen-Hsiung Chen, published in 19. The patent describes a DCT-based image compression algorithm, and would later be a cause of controversy in 2002 (see Patent controversy below). Patent 4,698,672, filed by Compression Labs' Wen-Hsiung Chen and Daniel J. Other companies cited as patent holders include AT&T (two patents) and Canon Inc. The JPEG specification also cites three other patents from IBM.
#JPEG IMAGE COMPRESSION STANDARDS . PDF CODE#
Rissanen – Multiplication-free multi-alphabet arithmetic code

The following patents provided the basis for its arithmetic coding algorithm. The JPEG specification cites patents from several companies.

Huffman's 1952 paper for its Huffman coding algorithm. Pratt as an influence on its quantization algorithm, and David A. The specification also cites a 1984 paper by Wen-Hsiung Chen and W.K. Fralick that described a fast DCT algorithm, as well as a 1978 paper by N.J. Their 1974 paper is cited in the JPEG specification, along with several later research papers that did further work on DCT, including a 1977 paper by Wen-Hsiung Chen, C.H. Natarajan of Kansas State University and K. Ahmed developed a practical DCT algorithm with T. The main basis for JPEG's lossy compression algorithm is the discrete cosine transform (DCT), which was first proposed by Nasir Ahmed as an image compression technique in 1972. The original JPEG specification published in 1992 implements processes from various earlier research papers and patents cited by the CCITT (now ITU-T) and Joint Photographic Experts Group. In 2000, the JPEG group introduced a format intended to be a successor, JPEG 2000, but it was unable to replace the original JPEG as the dominant image standard.
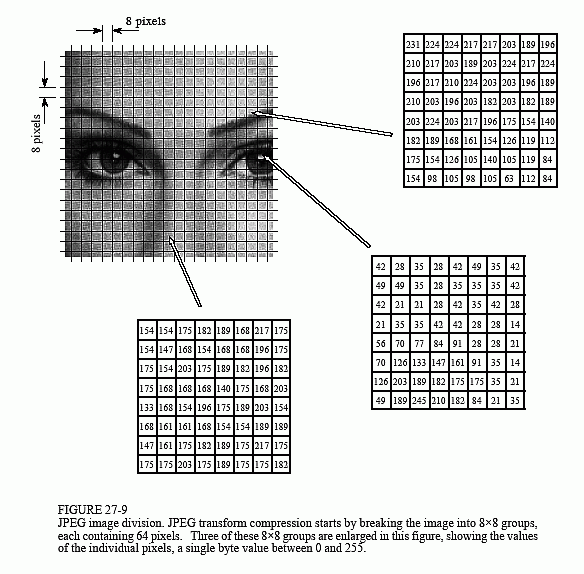
JPEG/JFIF supports a maximum image size of 65,535×65,535 pixels, hence up to 4 gigapixels for an aspect ratio of 1:1. JPEG files usually have a filename extension of. The MIME media type for JPEG is image/jpeg, except in older Internet Explorer versions, which provides a MIME type of image/pjpeg when uploading JPEG images. These format variations are often not distinguished, and are simply called JPEG. JPEG/ Exif is the most common image format used by digital cameras and other photographic image capture devices along with JPEG/ JFIF, it is the most common format for storing and transmitting photographic images on the World Wide Web. JPEG compression is used in a number of image file formats. JPEG was largely responsible for the proliferation of digital images and digital photos across the Internet, and later social media. JPEG's lossy image compression is based on the discrete cosine transform (DCT), a technique that was first proposed by Nasir Ahmed in 1972. The term "JPEG" is an acronym for the Joint Photographic Experts Group, which created the standard in 1992. Since its introduction in 1992, JPEG has been the most widely used image compression standard in the world, and the most widely used digital image format, with several billion JPEG images produced every day as of 2015. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG ( / ˈ dʒ eɪ p ɛ ɡ/ JAY-peg) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography.
Continuously varied JPEG compression (between Q=100 and Q=1) for an abdominal CT scan


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
